import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt19 Cambia la frecuencia de tus datos
Adentrémonos en la función resample, una herramienta esencial para quienes trabajan con datos y series temporales. En esta sesión, descubrirás cómo cambiar la frecuencia de tus datos temporales, ajustando series de minutos a horas o de días a semanas, abriendo un mundo de posibilidades para un análisis más profundo y significativo.
f = '../data/Temixco_2018_10Min.csv'
tmx = pd.read_csv(f,index_col=0,parse_dates=True)
tmx.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
DatetimeIndex: 52560 entries, 2018-01-01 00:00:00 to 2018-12-31 23:50:00
Data columns (total 7 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Ib 52423 non-null float64
1 Ig 52423 non-null float64
2 To 52560 non-null float64
3 RH 52560 non-null float64
4 WS 52560 non-null float64
5 WD 52560 non-null float64
6 P 52560 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(7)
memory usage: 3.2 MBtmx.plot(subplots=True);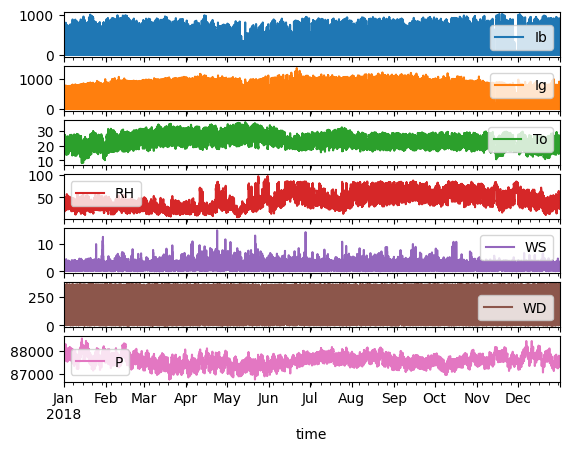
tmx.loc['2018-03-10','To'].plot(subplots=True,figsize=(12,3),style='o');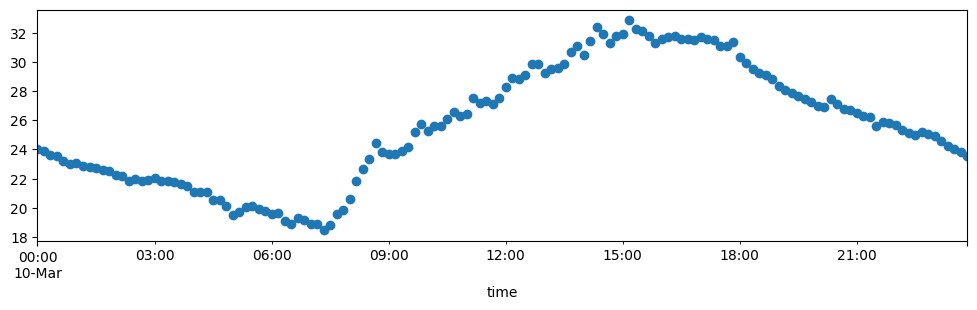
tmx[['To']].resample('H').max()| To | |
|---|---|
| time | |
| 2018-01-01 00:00:00 | 19.23 |
| 2018-01-01 01:00:00 | 19.25 |
| 2018-01-01 02:00:00 | 18.24 |
| 2018-01-01 03:00:00 | 17.49 |
| 2018-01-01 04:00:00 | 16.58 |
| ... | ... |
| 2018-12-31 19:00:00 | 22.39 |
| 2018-12-31 20:00:00 | 19.58 |
| 2018-12-31 21:00:00 | 19.29 |
| 2018-12-31 22:00:00 | 18.94 |
| 2018-12-31 23:00:00 | 18.61 |
8760 rows × 1 columns
tmx[['To']].resample('H',closed="right").max()| To | |
|---|---|
| time | |
| 2017-12-31 23:00:00 | 18.70 |
| 2018-01-01 00:00:00 | 19.23 |
| 2018-01-01 01:00:00 | 19.25 |
| 2018-01-01 02:00:00 | 18.24 |
| 2018-01-01 03:00:00 | 17.49 |
| ... | ... |
| 2018-12-31 19:00:00 | 21.87 |
| 2018-12-31 20:00:00 | 19.49 |
| 2018-12-31 21:00:00 | 19.11 |
| 2018-12-31 22:00:00 | 18.94 |
| 2018-12-31 23:00:00 | 18.51 |
8761 rows × 1 columns
tmx.loc['2018-03-10','To'].plot(subplots=True,figsize=(12,3),style='.')
tmx.loc['2018-03-10','To'].resample('H').max().plot(subplots=True,
figsize=(12,3),
style='o',
color='red',
alpha=0.7)array([<Axes: xlabel='time'>], dtype=object)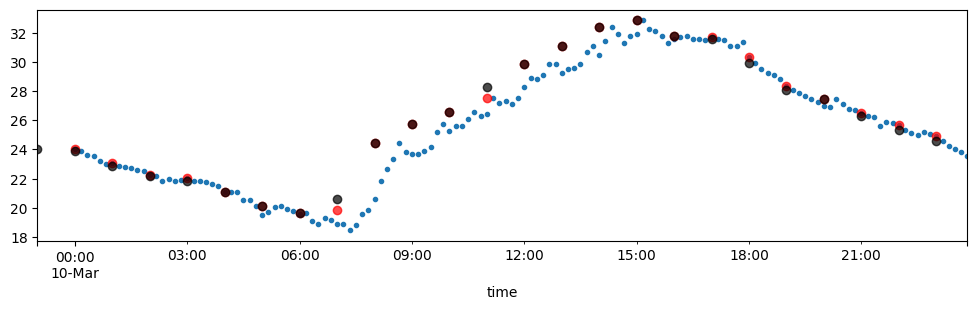
tmx.loc['2018-03-10','To'].plot(subplots=True,figsize=(12,3),style='.')
tmx.loc['2018-03-10','To'].resample('H').max().plot(figsize=(12,3),
style='o',
color='red',
alpha=0.7)
tmx.loc['2018-03-10','To'].resample('H').mean().plot(figsize=(12,3),
style='*',
color='black',
alpha=0.7)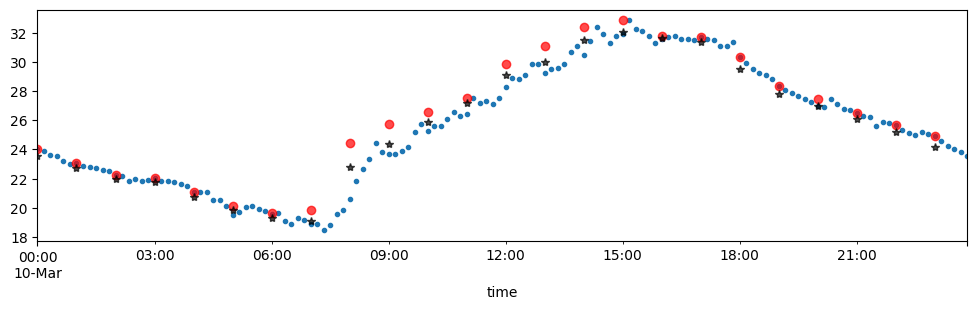
tmx.To.resample('D').mean()time
2018-01-01 21.073333
2018-01-02 19.813264
2018-01-03 19.910069
2018-01-04 19.705417
2018-01-05 20.782639
...
2018-12-27 20.374861
2018-12-28 19.778750
2018-12-29 20.654167
2018-12-30 20.726944
2018-12-31 20.230903
Freq: D, Name: To, Length: 365, dtype: float64tmx.To.resample('Y').agg(['mean','std','max','min','sum'])| mean | std | max | min | sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| time | |||||
| 2018-12-31 | 22.838098 | 4.443339 | 35.87 | 8.16 | 1200370.41 |
tmx.To.resample('30S').max() # min, std, no funcionatime
2018-01-01 00:00:00 18.70
2018-01-01 00:00:30 NaN
2018-01-01 00:01:00 NaN
2018-01-01 00:01:30 NaN
2018-01-01 00:02:00 NaN
...
2018-12-31 23:48:00 NaN
2018-12-31 23:48:30 NaN
2018-12-31 23:49:00 NaN
2018-12-31 23:49:30 NaN
2018-12-31 23:50:00 17.75
Freq: 30S, Name: To, Length: 1051181, dtype: float64tmx.To.resample('30S').interpolate()time
2018-01-01 00:00:00 18.7000
2018-01-01 00:00:30 18.7125
2018-01-01 00:01:00 18.7250
2018-01-01 00:01:30 18.7375
2018-01-01 00:02:00 18.7500
...
2018-12-31 23:48:00 17.7980
2018-12-31 23:48:30 17.7860
2018-12-31 23:49:00 17.7740
2018-12-31 23:49:30 17.7620
2018-12-31 23:50:00 17.7500
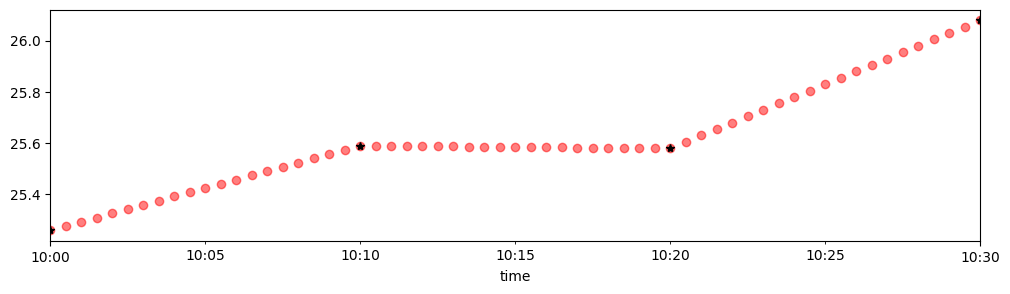
Freq: 30S, Name: To, Length: 1051181, dtype: float64tmx.loc['2018-03-10 10:00':'2018-03-10 10:30','To'].resample('30S').interpolate().plot(figsize=(12,3),
style='o',
color='red',
alpha=0.5
)
tmx.loc['2018-03-10 10:00':'2018-03-10 10:30','To'].plot(style='*',
color='k')