import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from dateutil.parser import parse23 Tipos de gráficas
En esta sección del curso, exploraremos las técnicas visuales disponibles en Matplotlib para representar datos por pares, o Pairwise data.
Desde el gráfico de líneas hasta herramientas como fill_between y stackplot, descubriremos cómo cada tipo de gráfico nos brinda una perspectiva única sobre la relación entre dos variables cuantitativas.
f = '../data/Cuernavaca_1dia_comas.csv'
cuerna = pd.read_csv(f,index_col=0,parse_dates=True)
cuerna.head()| To | Ws | Wd | P | Ig | Ib | Id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tiempo | |||||||
| 2012-01-01 00:00:00 | 19.3 | 0.0 | 26 | 87415 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2012-01-01 01:00:00 | 18.6 | 0.0 | 26 | 87602 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2012-01-01 02:00:00 | 17.9 | 0.0 | 30 | 87788 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2012-01-01 03:00:00 | 17.3 | 0.0 | 30 | 87554 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2012-01-01 04:00:00 | 16.6 | 0.0 | 27 | 87321 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(cuerna.To)
ax.set_title('plot')Text(0.5, 1.0, 'plot')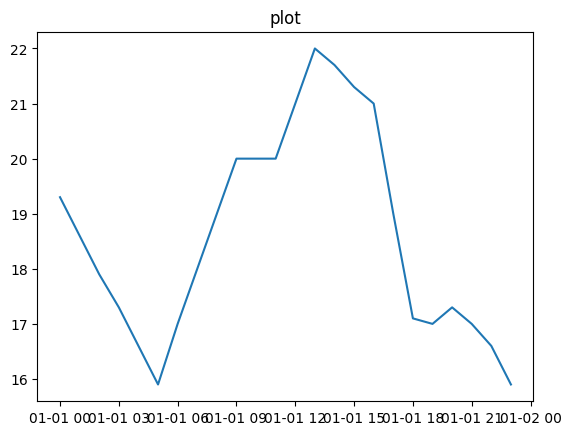
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(cuerna.index,cuerna.To)
ax.set_title('Scatter')Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Scatter')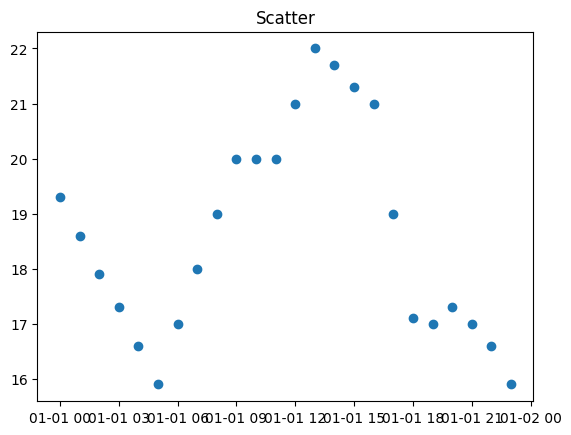
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# f1 = parse("2012-01-01")
# f2 = f1 + pd.Timedelta("10H")
ax.bar(cuerna.index,cuerna.To)
# ax.bar(cuerna.index,cuerna.To,width=1/25)
ax.set_title('Bars')
# ax.set_xlim(f1,f2)Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Bars')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
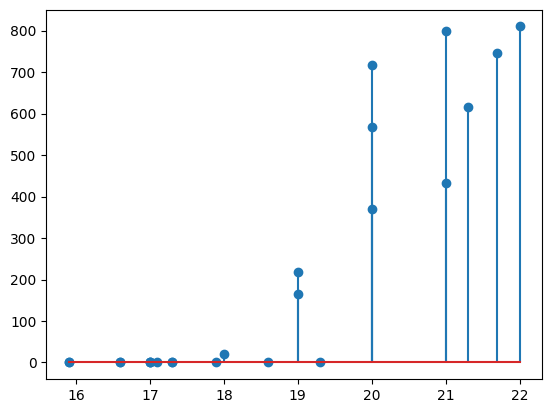
ax.stem(cuerna.To)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.fill_between(cuerna.index,cuerna.To.mean(),cuerna.To)
ax.plot(cuerna.To,'r-')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.stairs(cuerna.To)
Por supuesto hay que escoger cada tipo de gr’afica de acuerdo a los datos y lo que queremos transmitir.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(cuerna.To, cuerna.Ig)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.stem(cuerna.To, cuerna.Ig)